- This page was created by volunteers like you!
- Help us make it even better. To learn more about contributing to MEpedia, click here.
- Join the movement
- Visit #MEAction to find support or take action. Donate today to help us improve and expand this project.
- Congratulations!
- MEpedia has got over 30 million views as of August 2022!
Two-day cardiopulmonary exercise test
Two-day cardiopulmonary exercise test or 2-day CPET is a procedure which assesses exercise capacity and recovery by performing two exercise tests 24 hours apart.[1] The hypothesis is that ME/CFS patients display a characteristic deterioration in exercise capacity on the second test, a finding that has been reported by multiple research groups.[2][3][4]
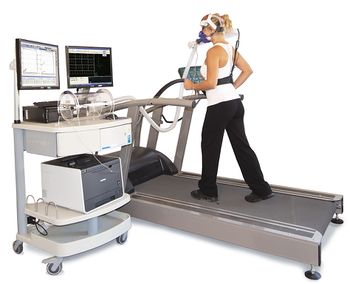
The maximal, symptom-limited cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET) is considered the gold standard for measuring physical capacity.[5][6] This test measures gas exchange parameters using a mouthpiece or mask, while participants exercise on a treadmill or stationary bicycle with a controlled increase in resistance or power output. It is commonly used to measure the fitness level of athletes, as well as patients with cardiopulmonary disease.[7] In these populations, CPET measures are highly reliable and reproducible.[1] Exercise physiologists however have noted that ME/CFS patients are unable to reproduce these measurements on consecutive days, despite meeting criteria for maximal effort.[8] According to a 2015 report by The National Academy of Medicine, “ME/CFS patients have significantly lower results on CPET 2 than on CPET 1 on one or more of the following parameters: VO2max, VO2 at ventilatory threshold and maximal workload or workload at ventilatory threshold.”[9]
Specifically, VO2Max is the true maximal oxygen consumption of a participant, VO2Peak is the recorded maximal oxygen consumption of a participant and VO2 at ventilatory threshold is the oxygen consumption at the first key threshold (VT or VT1), otherwise known as the gas exchange threshold (GET). This threshold is the point at which carbon dioxide output (VCO2) and oxygen consumption no longer increase linearly, which occurs at 40-75% of VO2Max, depending on the fitness and health of the participants. The VT1 is commonly determined using the V-slope method, which notes the point of non linearity when VO2 is plotted against VCO2. The VT1 can also be indicated using the ventilatory equivalent method, plotting VE/VO2 and VE/VCO2 on the same graph and noting the point where VE/VO2 increases significantly, while VE/VCO2 remains flat (where VE is minute ventilation, which is the total amount of gas inhaled or exhaled from the lungs per minute). While the VT1 is primarily determined by peripheral metabolic factors, it is not synonymous with the lactate threshold which is the point at which lactate starts to accumulate significantly in the blood. The lactate threshold is not only dependent on lactate/pyruvate equilibrium inside the muscle cells, but the kinetics of lactate transport into and out of cells. Nor is VT1 synonymous with the onset of acidosis which is additionally affected by pH buffering within the cell and the circulatory system. It is also important to point out that this gas exchange threshold is not caused by shortness of breath, nor hyperventilation, since neither hypocapnia nor hypercapnia occur at this threshold. There is however, a second ventilatory threshold (VT2) otherwise known as the respiratory compensation point (RCP), and typically occurs at 85-90% of VO2Max. This respiratory compensation occurs when a significant reduction in blood or cerebrospinal fluid pH activates chemoreceptors, which stimulate the respiratory centre of the brain, leading to compensatory hyperventilation to help restore the pH balance.
According to researchers in the field, the abnormal results of ME/CFS patients on the 2-day CPET reflect post-exertional malaise (PEM), a marked symptom exacerbation after exercise thought to be characteristic of this condition.[2] The 2015 report by National Academy of medicine indicated that the 2-day CPET protocol can be used as an objective indicator that physical exertion decreases subsequent function in patients with ME/CFS, for example in obtaining social security disability.[9] The 2-day CPET protocol however is not required in making the diagnosis of ME/CFS. Some have expressed concern that exercise tests may significantly worsen the condition of ME/CFS patients.[9][10][11][4]
Evidence[edit | edit source]
Mark VanNess, Christopher Snell and Staci Stevens of the University of the Pacific, Stockton, CA, were the first to study the two-day CPET procedure in patients with ME/CFS. In a 2007 study published in the Journal of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, they compared six ME/CFS patients with six controls. At the first CPET there were no major differences between the two groups. At the second CPET however, ME/CFS patients reached significantly lower peak oxygen consumption (VO2Peak) and oxygen consumption at aerobic threshold.[8]
In 2010, a Dutch research group including Ruud Vermeulen and Frans Visser used the 2-day CPET in a study with 15 female ME/CFS and 15 healthy controls. Patients reached the aerobic threshold and the maximal exercise at much lower oxygen consumption than controls, an effect that was magnified during the second-day exercise test. Since levels of creatine kinase in the blood and oxidative phosphorylation in mononuclear cells were normal in patients before and after exercise, Vermeulen et al. speculated that the lowered anaerobic threshold was not so much a result of mitochondrial insufficiency, but of impaired oxygen transport to the muscles.[12]
In 2013, Snell, Stevens and VanNess tested the 2-day CPET procedure in a larger sample of 51 ME/CFS patients and 10 healthy controls. Once again, there were no sufficient differences between the groups at the first CPET. During the exercise test on the second day however, ME/CFS patients showed much lower oxygen consumption and workload at peak exercise and at aerobic threshold. Group differences were not due to lack of effort since most participants attained the ventilatory threshold and achieved a respiratory exchange ratio of greater than or equal to 1.1.[4]
In 2014, the research group of Betsy Keller used the 2-day CPET protocol in a study involving 22 ME/CVS patient. A decline on several physiological measures was found (see table), while the respiratory exchange ratio indicated maximum efforts by participants during both exercise tests.[2]
This group followed this research up with a study of a single pair of monozygotic twins in 2016.[13]
| Physiological changes between first and second exercise test during 2-day CPET procedure in patients with ME/CFS (bold indicates statistical significance) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of ME/CFS patients | VO2 peak | VO2 at VT | Workload peak | Workload at VT | HR peak | O2pulse at VT | |
| VanNess et al. 2007.[8] | 6 | -22% | -26% | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| Vermeulen et al. 2010. [12] | 15 | -6.3% | -7.0% | -5.3% | -7.0% | -1.9% | -8.8% |
| Snell et al. 2013.[4] | 51 | -5% | -10.8% | -7.2% | -11% (revised) | ? | ? |
| Keller et al. 2014.[2] | 22 | -13.8% | -15.8% | -12.5% | -21.3% | -5.9% | -12.6% |
| Giloteaux et al. 2016.[13] | 1 (monozygotic twin) | 0% | -13.4% | 0% | -25% | +7.4% | -19% (calculated) |
| Hodges et al. 2018.[3] | 10 | +5.3% | +6.1% | -6.7% | -11.4% | -0.6% | +7% (calculated) |
| Nelson et al. 2019.[14] | 16 | +0.4% | -3.1% | -1.2% | -17.4% | -0.5% | +2% (calculated) |
| Lien et al. 2019.[15] (numerical estimates) | 18 | -5% | -6% | -2% | -7% | +1.5% | ? |
| van Campen 2020.A[16] (males) | 25 | -10% | -22% | -10% | -30% | -5% | -16% (calculated) |
| van Campen 2020.B[17] (females) | 31 ("mild" cases) | -6% | -21% | -10% | -26% | -3% | ? |
| van Campen 2020.B[17] (females) | 31 ("moderate" cases) | -11% | -21% | -16% | -31% | -6% | ? |
| van Campen 2020.B[17] (females) | 20 ("severe" cases) | -12% | -19% | -19% | -33% | -7% | ? |
| Davenport 2020.[18] | 51 | -5% | -10% | -9% | -11% | -3% | -7% (calculated) |
| van Campen 2021.[19] (males) | 26 | -12% | -27% | -10% | -27% | -7% | -17% (calculated) |
| van Campen 2021.[20] (females) | 50 | -10% | -23% | -11% | -30% | -4% | -15% (calculated) |
| Keller 2024.[21] | 84 | -5.3%(calculated) | -6.8%(calculated) | -5.5%
(calculated) |
-9.4%(calculated) | ||
In 2017, a research team form New Zealand compared the physiological responses during a 2-day CPET, in ten patients with ME/CFS, seven patients with Multiple Sclerosis (MS) and seventeen healthy controls. Curiously peak oxygen increased at the second exercise test in ME/CFS patients, but there was a significant reduction noticeable in workload at aerobic threshold, a decline that was not seen in MS-patients or healthy controls. According to the authors:
“differences between MS and CFS/ME responses only became evident after a second maximal exercise test, thus suggesting that a repeated protocol is required to not only distinguish CFS/ME from HC, but also from other fatigue-related conditions, who may not suffer from post-exertional malaise and have a differing delayed fatigue profile.”[3]
In 2019 the 2-day CPET procedure was tested by an Australian research team of Nelson and colleagues. They found a significant larger reduction in workload at the ventilatory threshold in patients with ME/CFS compared to healthy controls. A percentage change of −6.3% to −9.8% provided good sensitivity and specificity, indicating this test has the potential to become a biomarker for ME/CFS. However, the sample size of this study was small (16 ME/CFS patients), the control group consisted only of healthy persons (instead of patients with other chronic illnesses) and no significant difference was found in VO2 at the ventilatory threshold.[14]
A Norwegian study published in 2019 also reported a significant larger reduction in workload at the ventilatory threshold in 18 patients with ME/CFS compared to healthy controls, although this was not the case for peak values or VO2 measurement at the ventilatory threshold. The authors also measured arterial lactate concentrations, every 30 seconds during the exercise tests. Lactate was higher per power output per kg in patients than controls and the differences increased significantly at the second exercise test. In the healthy controls lactate concentration at the ventilatory threshold decreased while this was not the case in ME/CFS patients, suggesting a problem in lactate clearance ability.[15]
Researchers from the Workwell Foundation published in 2019, a case series of six women, who underwent the 2-day CPET. This study compared two healthy participants, one active, the other sedentary, two ME/CFS patients, one high functioning with high VO2peak, another with low VO2Peak, with a patient suffering from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and another suffering from MS.[22] The healthy participants and the MS patient reproduced or improved their exercise parameters, namely VO2, workload, heart-rate and minute ventilation at both the ventilatory threshold and peak exercise. The HIV patient reproduced all of these findings except peak workload and peak minute ventilation. The ME/CFS patients were unable to reproduce VO2, workload, heart rate or minute ventilation at the ventilatory threshold. These results continue to suggest that the inability to reproduce workload at the ventilatory threshold is specific to ME/CFS patients, but patients with other fatiguing conditions will need to be tested to confirm this. This study was followed up in 2020 with 51 patients and 10 controls, focusing on additional statistical analysis and discussing the meaning of test-retest reliability in the context of ME/CFS. The main positive finding was a significant group*test (difference) in work rate at the ventilatory threshold. [18]
In 2020, researchers from Stichting Cardio Zorg, a cardiology clinic in the Netherlands published two studies of clinical 2-day CPET results for ME/CFS patients with exercise intolerance. The first study consisted of male patients, to see whether the results from previous studies which had predominantly female patients would be replicated.[16] A second study focused on female patients with differing severity, which were subgrouped according to: “Symptom severity impact must result in a 50% or greater reduction in a patient’s premorbid activity level for a diagnosis of ME. Mild: approximately 50% reduction in activity, moderate: mostly housebound, severe: mostly bedbound and very severe: bedbound and dependent on help for physical functions”.[17] This research was followed up in 2021 with a retrospective clinical comparison between 26 male idiopathic chronic fatigue (ICF) cases who did not suffer from PEM and 25 male ME/CFS patients who satisfied the 2011 ME International Consensus Criteria and the 1994 Center for Disease Control criteria for CFS. [19] Notably, most ME/CFS patients had a decline in VO2 and workload performance at peak and the ventilatory threshold on the second day, compared to all idiopathic chronic fatigue cases who were able to match or exceed their first day performance. The authors concluded that this decline in performance on the second day was disease-specific.[19] A related comparison was performed for female patients with similar results.[20] However there were several ICF patients that also had a reduction in peak workload and workload at the ventilatory threshold, despite the overall trend for an increase for ICF patients and a decrease for ME/CFS patients.
Unpublished studies have reported negative results for the repeated CPET procedure. In her thesis, Tessa-Maree Nielsen[23] at the Massey University, New Zealand, performed the second exercise test 48 hours and 72 hours later, instead of the usual 24 hours. The study did not find significant reductions of workload at the ventilatory threshold in ME/CFS patients compared to controls. The eight ME/CFS patients in the 72 hours group had a workload at ventilatory threshold that was slightly higher instead of lower than during the first test. In a 2018 presentation,[24] Ruud Vermeulen reported to have data on approximately 500 ME/CFS patients who performed the repeated CPET procedure. He stated the test on the second day did not show any difference in VO2max compared to the first day, as shown in the graphs he presented.
Two-Day CPET studies have also considered other clinical groups, including Gulf-War-Syndrome[25] and Sarcoidosis.[26] The study of Gulf-War-Syndrome patients did not reveal any significant group by time effects and in particular, no time effects at VT1. The study of Sarcoidosis patients did not find any group by time effects, however they focused on peak performance and ignored differences in performance at sub-maximal thresholds such as VT1. In addition, the study of Sarcoidosis patients did find an exercise effect on several biomarkers, however changes in these markers were not related to self-reported fatigue. A 2023 conference abstract examined preliminary data from 2-day CPETs of LongCOVID patients [27] and found there was no difference in peak workrate and peak VO2 relative to day one. However the key finding across all ME/CFS studies is a reduction in workrate at VT1, and it is uncertain if that study analysed such data.
Use as a Biomarker[edit | edit source]
Snell et al. suggested 2-day CPET could be used "diagnostically as an objective indicator of an abnormal postexertion response and possibly even a biomarker for the condition."[4] Using the data from the two exercise tests, their research team was able to correctly classify 95% of the total sample, as a patient or healthy control.
Criticism[edit | edit source]
While a unique reduction in physiological capacity was observed in ME/CFS by several studies and different research groups, sample sizes were rather small and disagreement exists on which physiological measure accurately displayed ME/CFS patients’ abnormal exertional response.[2]
Another objection to the 2-day CPET as a biomarker for ME/CFS was raised by Snell et al themselves. They suggested it might be unethical[4] to use this method to detect ME/CFS patients since many of these patients might suffer relapse as a result of exercise testing. In their 2010 study, 60% of ME/CFS patients reported that it took them more than 5 days to recover from a single (maximal) CPET. It is therefore possible that in some ME/CFS patients a 2-day CPET might cause a long-lasting relapse. Science-reporter and ME/CFS patient Simon McGrath for example wrote: “You couldn’t pay me enough money to take even one max test. My last relapse, which took me nearly 2 years to get over, happened after way less than maximal exertion – a 2-day test is not for everyone."[28]
Others have noted that the CPET-procedure is not very practical. It cannot be used in patients with severe ME/CFS (thus excluding these patients from study) and because of cost and expertise, it may not be available to most clinicians.[29] CPET for ME/CFS is usually not covered by insurance and can cost hundreds of dollars.[30] For these reasons PEM is commonly assessed using self-reporting questionnaires.
Brian Vastag was able to prove his PEM was a severe symptom causing disability with CPET, winning his long term disability (LTD) claim.[31]
Cost and availability[edit | edit source]
- Workwell Foundation (United States, CA)
- Betsy Keller at Ithaca College (United States, NY) Cost is $2200. Because they are based in a college setting (not healthcare setting), they cannot process insurance (including Medicare or Medicaid), so the patient would need to work directly with their insurer about reimbursement. (private email)
- Laura Black at Hunter-Hopkins Center, Charlotte, NC
- Open Medicine Institute Clinic
- Physiologic 334 Scottsdale Drive, Robina, Gold Coast, Australia
- Many UK universities offer standard CPETs which can be adapted for patients with ME.
Talks and interviews[edit | edit source]
- 2013, CPET Presentation by Dr. Christopher Snell, Part ICPET Presentation by Dr. Christopher Snell, Part II
- 2014, Mark VanNess 'Exercise and ME/CFS' at Bristol Watershed. Part One
See also[edit | edit source]
Learn more[edit | edit source]
- The Workwell Foundation: Testing for Disability
- 2007, Legal and Scientific Considerations of the Exercise Stress Test
- 2013, Busted! Exercise Study Finds Energy Production System is Broken in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
- 2013, Repeat Test Reveals Dramatic Drop in ME/CFS Exercise Capacity
- 2018, Victory For ME Disability Claim – U.S. Court Upholds Plaintiff's Lawsuit After Being Denied Disability[31]
- 2019, Decoding the 2-day Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test (CPET) in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) by C. Christian
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Stevens, Staci; Snell, Chris; Stevens, Jared; Keller, Betsy; VanNess, J. Mark (2018). "Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test Methodology for Assessing Exertion Intolerance in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome". Frontiers in Pediatrics. 6: 242. doi:10.3389/fped.2018.00242. ISSN 2296-2360. PMC 6131594. PMID 30234078.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Keller, Betsy A.; Pryor, John Luke; Giloteaux, Ludovic (April 23, 2014). "Inability of myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients to reproduce VO₂peak indicates functional impairment". Journal of Translational Medicine. 12: 104. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-12-104. ISSN 1479-5876. PMC 4004422. PMID 24755065.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 3.2 Hodges, L. D.; Nielsen, T.; Baken, D. (July 2018). "Physiological measures in participants with chronic fatigue syndrome, multiple sclerosis and healthy controls following repeated exercise: a pilot study". Clinical Physiology and Functional Imaging. 38 (4): 639–644. doi:10.1111/cpf.12460. ISSN 1475-097X. PMID 28782878.
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Snell, C. R.; Stevens, S.R.; Davenport, T.E.; Van Ness, J.M. (June 27, 2013). "Discriminative Validity of Metabolic and Workload Measurements for Identifying People With Chronic Fatigue Syndrome". Physical Therapy. 93 (11): 1484–1492. doi:10.2522/ptj.20110368. ISSN 0031-9023.
- ↑ Chandra, Divay; Wise, Robert A.; Kulkarni, Hrishikesh S.; Benzo, Roberto P.; Criner, Gerard; Make, Barry; Slivka, William A.; Ries, Andrew L.; Reilly, John J. (December 2012). "Optimizing the 6-Min Walk Test as a Measure of Exercise Capacity in COPD". Chest. 142 (6): 1545–1552. doi:10.1378/chest.11-2702. ISSN 0012-3692. PMC 3515028. PMID 23364913.
- ↑ Demir, Rengin; Küçükoğlu, Mehmet Serdar (December 2010). "Evaluation of exercise capacity in pulmonary arterial hypertension". Turk Kardiyoloji Dernegi Arsivi: Turk Kardiyoloji Derneginin Yayin Organidir. 38 (8): 580–588. ISSN 1016-5169. PMID 21248462.
- ↑ Albouaini, Khaled; Egred, Mohaned; Alahmar, Albert; Wright, David Justin (November 2007). "Cardiopulmonary exercise testing and its application". Postgraduate Medical Journal. 83 (985): 675–682. doi:10.1136/hrt.2007.121558. ISSN 1469-0756. PMC 2734442. PMID 17989266.
- ↑ Jump up to: 8.0 8.1 8.2 Vanness, J. Mark; Snell, Christopher R.; Stevens, Staci R. (January 2007). "Diminished Cardiopulmonary Capacity During Post-Exertional Malaise". Journal of Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. 14 (2): 77–85. doi:10.1300/j092v14n02_07. ISSN 1057-3321.
- ↑ Jump up to: 9.0 9.1 9.2 Committee on the Diagnostic Criteria for Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome; Board on the Health of Select Populations; Institute of Medicine (2015). Beyond Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Redefining an Illness. The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US). ISBN 9780309316897. PMID 25695122.
- ↑ Nijs, J.; Van Oosterwijck, J.; Meeus, M.; Lambrecht, L.; Metzger, K.; Frémont, M.; Paul, L. (April 2010). "Unravelling the nature of postexertional malaise in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome: the role of elastase, complement C4a and interleukin-1beta". Journal of Internal Medicine. 267 (4): 418–435. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2009.02178.x. ISSN 1365-2796. PMID 20433584.
- ↑ VanNess, J. Mark; Stevens, Staci R.; Bateman, Lucinda; Stiles, Travis L.; Snell, Christopher R. (February 2010). "Postexertional malaise in women with chronic fatigue syndrome". Journal of Women's Health (2002). 19 (2): 239–244. doi:10.1089/jwh.2009.1507. ISSN 1931-843X. PMID 20095909.
- ↑ Jump up to: 12.0 12.1 Vermeulen, Ruud C. W.; Kurk, Ruud M.; Visser, Frans C.; Sluiter, Wim; Scholte, Hans R. (October 11, 2010). "Patients with chronic fatigue syndrome performed worse than controls in a controlled repeated exercise study despite a normal oxidative phosphorylation capacity". Journal of Translational Medicine. 8: 93. doi:10.1186/1479-5876-8-93. ISSN 1479-5876. PMC 2964609. PMID 20937116.
- ↑ Jump up to: 13.0 13.1 Giloteaux, Ludovic; Hanson, Maureen R.; Keller, Betsy A. (October 10, 2016). "A Pair of Identical Twins Discordant for Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Differ in Physiological Parameters and Gut Microbiome Composition". American Journal of Case Reports. 17: 720–729. doi:10.12659/AJCR.900314. ISSN 1941-5923. PMC 5058431. PMID 27721367.
- ↑ Jump up to: 14.0 14.1 Nelson, Maximillian J.; Buckley, Jonathan D.; Thomson, Rebecca L.; Clark, Daniel; Kwiatek, Richard; Davison, Kade (March 14, 2019). "Diagnostic sensitivity of 2-day cardiopulmonary exercise testing in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome". Journal of Translational Medicine. 17 (1): 80. doi:10.1186/s12967-019-1836-0. ISSN 1479-5876. PMC 6417168. PMID 30871578.
- ↑ Jump up to: 15.0 15.1 Lien, Katarina; Johansen, Bjørn; Veierød, Marit B.; Haslestad, Annicke S.; Bøhn, Siv K.; Melsom, Morten N.; Kardel, Kristin R.; Iversen, Per O. (2019). "Abnormal blood lactate accumulation during repeated exercise testing in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome". Physiological Reports. 7 (11): e14138. doi:10.14814/phy2.14138. ISSN 2051-817X.
- ↑ Jump up to: 16.0 16.1 van Campen, C. (Linda) M. C.; Rowe, Peter C.; Visser, Frans C. (2020). "Validity of 2-Day Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing in Male Patients with Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome". Advances in Physical Education. 10 (01): 68–80. doi:10.4236/ape.2020.101007. ISSN 2164-0386.
- ↑ Jump up to: 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 van Campen, C (Linda) MC; Rowe, Peter C.; Visser, Frans C. (June 30, 2020). "Two-Day Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing in Females with a Severe Grade of Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Comparison with Patients with Mild and Moderate Disease". Healthcare. 8 (3): 192. doi:10.3390/healthcare8030192. ISSN 2227-9032.
- ↑ Jump up to: 18.0 18.1 Davenport, Todd E.; Stevens, Staci R.; Stevens, M. A. Jared; Snell, Christopher R.; Van Ness, J. Mark (June 16, 2020). "Properties of measurements obtained during cardiopulmonary exercise testing in individuals with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome". Work: 1–10. doi:10.3233/WOR-203170.
- ↑ Jump up to: 19.0 19.1 19.2 van Campen, C. (Linda) M. C.; Visser, Frans C. (June 2021). "Comparing Idiopathic Chronic Fatigue and Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) in Males: Response to Two-Day Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing Protocol". Healthcare. 9 (6): 683. doi:10.3390/healthcare9060683.
- ↑ Jump up to: 20.0 20.1 van Campen, C. (Linda) M. C.; Visser, Frans C. (June 2021). "Female Patients with Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome or Idiopathic Chronic Fatigue: Comparison of Responses to a Two-Day Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing Protocol". Healthcare. 9 (6): 682. doi:10.3390/healthcare9060682.
- ↑ Keller, Betsy; Receno, Candace N.; Franconi, Carl J.; Harenberg, Sebastian; Stevens, Jared; Mao, Xiangling; Stevens, Staci R.; Moore, Geoff; Levine, Susan; Chia, John; Shungu, Dikoma (July 5, 2024). "Cardiopulmonary and metabolic responses during a 2-day CPET in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome: translating reduced oxygen consumption to impairment status to treatment considerations". Journal of Translational Medicine. 22 (1): 627. doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05410-5. ISSN 1479-5876. PMC 11229500. PMID 38965566.
- ↑ Larson, Benjamin; Davenport, Todd E.; Stevens, Staci R.; Stevens, Jared; Van Ness, J. Mark; Snell, Christopher R. (October 2019). "Reproducibility of Measurements Obtained During Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing in Individuals With Fatiguing Health Conditions: A Case Series". Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy Journal. 30 (4): 145–152. doi:10.1097/CPT.0000000000000100. ISSN 1541-7891.
- ↑ Nielsen TM. The Timeline of Post Exertional Malaise in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. 2018.
- ↑ Presentation Ruud Vermeulen (03-06-2018). Minute 34.00.
- ↑ Lindheimer, Jacob B.; Alexander, Thomas; Qian, Wei; Klein‐Adams, Jacquelyn C.; Lange, Gudrun; H. Natelson, Benjamin; Cook, Dane B.; Hill, Helene Z.; Falvo, Michael J. (September 2020). "An analysis of 2‐day cardiopulmonary exercise testing to assess unexplained fatigue". Physiological Reports. 8 (17). doi:10.14814/phy2.14564. PMID 32889791.
- ↑ Braam, A.W.E.; de Haan, S.N.; Vorselaars, A.D.M.; Rijkers, G.T.; Grutters, J.C.; van den Elshout, F.J.J.; Korenromp, I.H.E. (October 2013). "Influence of repeated maximal exercise testing on biomarkers and fatigue in sarcoidosis". Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 33: 57–64. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2013.05.006.
- ↑ Stringer, William; Heffernan, Carly (October 2023). "UTILITY OF 2-DAY CARDIOPULMONARY EXERCISE TESTING PROTOCOL IN LONG-HAUL COVID (LHC) PATIENTS: PRELIMINARY DATA". Chest. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.3724.
- ↑ "Declining Production: Exercise Study Reveals Broad Declines in Energy Output in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome - Health Rising". Health Rising. May 20, 2014. Retrieved August 17, 2018.
- ↑ https://www.commondataelements.ninds.nih.gov/Doc/MECFS/03_Fatigue_Subgroup_CDE_Draft_Recommendations.pdf
- ↑ Cotler, Joseph; Holtzman, Carly; Dudun, Catherine; Jason, Leonard A. (September 11, 2018). "A Brief Questionnaire to Assess Post-Exertional Malaise". Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland). 8 (3). doi:10.3390/diagnostics8030066. ISSN 2075-4418. PMID 30208578.
- ↑ Jump up to: 31.0 31.1 Tillman, Adriane (June 4, 2018). "Victory for ME Disability Claim - U.S. Court Upholds Plaintiff's Lawsuit After Being Denied Disability". #MEAction. Retrieved February 2, 2019.

